asdf- Link: video link
Consider a \((n,n-1)\) linear binary code
- \(m=[m_1, m_2, ..., m_{n-1}]\) –> (Encoding) –> \(c=[m_1, m_2, ..., m_{n-1}, p]\), where \(p\) is a parity-check bit.
- \(p = m_1 \oplus m_2 \oplus \cdots \oplus m_{n-1}\), where \(\oplus\) denotes XOR gate.
Ex) (3,2) SPC code:
| m | c |
|---|---|
| 0 0 | 000 |
| 0 1 | 011 |
| 1 0 | 101 |
| 1 1 | 110 |
\[G = \begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{I}_{n-1} & | & 1_{n-1} \end{bmatrix}\in\{0,1\}^{n-1,n} \] \[H = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 & ... & 1 \end{bmatrix}\in\{0,1\}^{n}\]
We can use this into encoding: \(c = \mathbf{mG}\) and \(e=\mathbf{c}^T\mathbf{H}\).
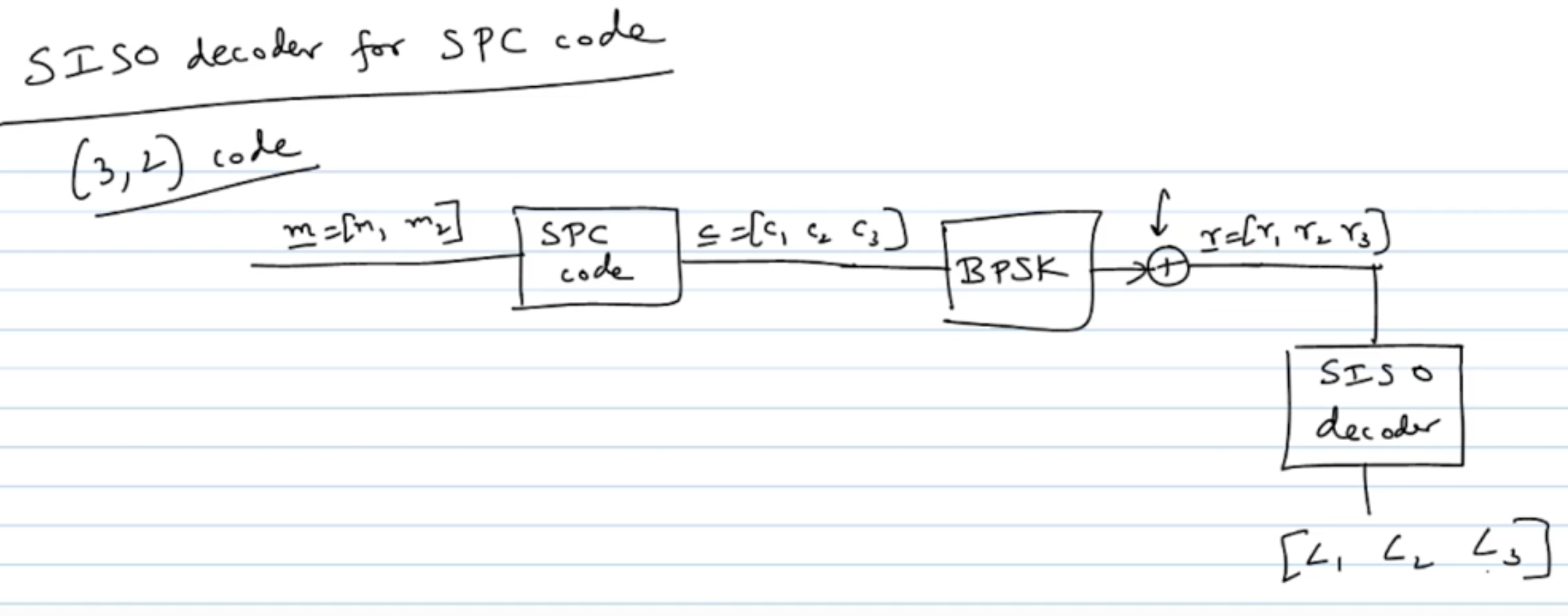
- Q: \(L_1\) is intrinsic of \(r_1\). What do \(r_2\) and \(r_3\) say about \(c_1\)?
- A: \(c_1 = c_2\oplus c_3\) (parity check condition)
Maximum likelihood decoding
\[\ell_2 = \log\frac{\Pr (c_2=0|r_2)}{\Pr (c_2=1|r_2)} = \log\frac{p_2}{1-p_2}\] \[\ell_3 = \log\frac{\Pr (c_3=0|r_2)}{\Pr (c_3=1|r_3)} = \log\frac{p_3}{1-p_3}\]
Given \(p_2\) and \(p_3\), what is \(\Pr(c_1=0|r_2, r_3)\)?
\[p_1 = \Pr(c_1=0|r_2, r_3) = p_2p_3 + (1-p_2)(1-p_3)\]
Extrinsic Log-Likelihood Ratio (LLR)
- \(\log\frac{p_1}{1-p_1}\): extrinsic LLR –> the following interesting holds
\[ \frac{p_1 - (1-p_1)}{p_1 + (1-p_1)} = \frac{p_2 - (1-p_2)}{p_2 + (1-p_2)}\frac{p_3 - (1-p_3)}{p_3 + (1-p_3)} \]
\[ \frac{1-(\frac{1-p_1}{p_1})}{1+(\frac{1-p_1}{p_1})} = \frac{1-e^{-l_{ext,1}}}{1+e^{-l_{ext,1}}} = \frac{1-e^{-l_{ext,2}}}{1+e^{-l_{ext,2}}} \cdot \frac{1-e^{-l_{ext,2}}}{1+e^{-l_{ext,2}}} \]
\[ \tanh(\ell_{ext,1}/2) = \tanh(\ell_{ext,2}/2) \cdot \tanh(\ell_{ext,3}/2) \]
Note: Since the hyperbolic tangent function is a odd function, \(\text{sgn}(\ell_1) = \text{sgn}(\ell_2) * \text{sgn}(\ell_3)\).